COOPERATION BETWEEN RUSSIA AND INDIA
5)Connectivity
International North South Transit Corridor (INSTC)
What is INSTC?
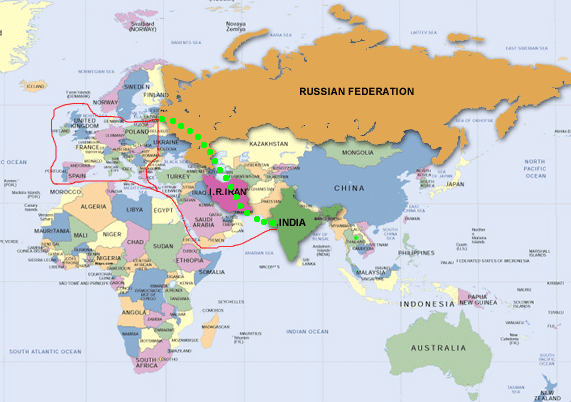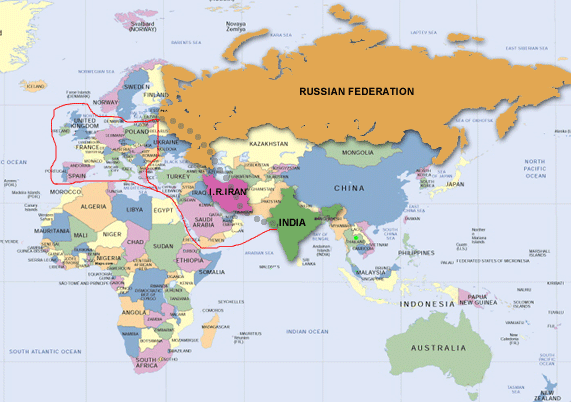
It is a multinodel(ship, rail, and road route) project for moving frieght between India to Russis through Central Asis and Europe
Why INSTC ?
- Lack of connectivity to central asis due to Pakistan factor
- Reduces both time (by 30%) and coast (by 40%)
- Its a project to tackle growing influence of China in Central Asian region
- INCTC is in compliance with Connect Central Asia Policy and look west policy
Connected regions
- INSTC is a multi-modal transportation route linking Indian Ocean and Persian Gulf to the Caspian Sea via Iran, and then onwards to northern Europe via St. Petersburg in Russia
Participating Countries
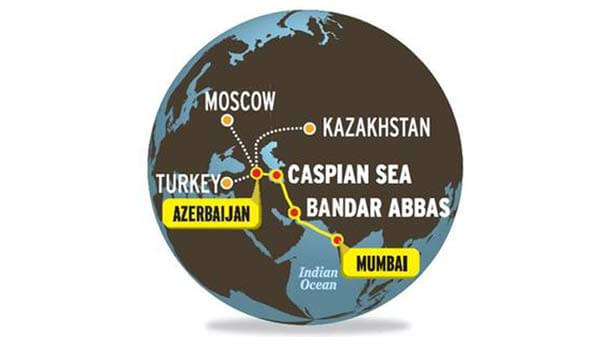
The route primarily involves moving freight from India, Iran, Azerbaijan and Russia via ship, rail and road. The objective of the corridor is to increase trade connectivity between major cities such as Mumbai, Moscow, Tehran, Baku, Bandar Abbas, Astrakhan, Bandar Anzali and etc.
INSTC Route
Constraints of INSTC
- Problems related to customs procedure and documentation remain.
- Issues relating to the funding of the infrastructure needed.
- Low level of existing containerisation on the route.
- Lack of a common border crossing rules among the participating nations.
- Higher tariff by rail vis-à-vis road transport relating to movement from Bandar Abbas.
- Wagon shortages.
- Security problem emanating from Islamic insurgents east, and west of the route, and associated hurdle of high insurance costs
Two other agreements that compliment INSTC
#Ashgabat Agreement
- The agreement was signed in the year 2011
- Objective : Enhancing connectivity in the Eurasian region and synchronising it with the International North South Transport Corridor (INSTC), Eurasian Railway Connectivity, Hajigak-Chabahar Railway and also the other transport corridors.
- The Ashgabat agreement establishes a transport and transit corridor between countries in the Persian Gulf and the Central Asia.
- It derives its name from the capital city of Turkmenistan, Ashgabat
- The agreement came into force in 2016.
- India in 2018 joined the Ashgabat agreement with the approval of the founding members.
- Pakistan has also made bids to join the Agreement from November 2016 but are yet to be approved by existing members.
- Signaturies as of 2018 : Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Iran, India and Oman
#Trilateral Transport and Transit Corridor
- Members : India, Iran and Afghanistan…
6)Civil Nuclear Agreement
- Russia is an important partner in peaceful uses of nuclear energy and it recognizes India as a country with advanced nuclear technology with an impeccable non-proliferation record.
- In December 2014, Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and Russia’s Rosatom signed the Strategic Vision for strengthening cooperation in peaceful uses of atomic energy between India and Russia. Russia has proposed a plan to involve India in building Russian-designed nuclear power stations in third countries.
- The cooperation is to be extended to the area of joint extraction of natural uranium and the production of nuclear fuel and atomic waste elimination. Russia has also offered to build over 20 nuclear power units in India, up from the 12 offered earlier.
- The Russian proposal to jointly build nuclear power plants is significant, considering that Rosatom-the State-owned Russian nuclear utility-has 29 nuclear reactors in various stages of planning and construction in more than a dozen countries (the largest internationally).
- These include in Jordan, Hungary, Egypt, Iran, Finland, Turkey and Argentina.
- The new proposals, offered by the Russians as a plank to build on their head-start in the Indian nuclear market, are expected to lay the foundation for what is being termed by Moscow as “long-term, mutually beneficial cooperation in the nuclear sector.
- The Russian proposal builds on a package of inter-governmental and inter-departmental documents signed on the sidelines of President Vladimir Putin’s visit to India late last year, as part of a ‘strategic vision for strengthening Indian-Russian cooperation in the peaceful use of nuclear power’.
- The nuclear cooperation includes building on negotiations to sign an advance contract for the design of the third and fourth reactor units to come up at the Kudankulam site in Tamil Nadu.
- Russia, in accordance with an inter-governmental agreement of 1988 and a supplement to it signed in 1998, is building the Kudankulam nuclear power project, the first 1,000 MWe (megawatt electric) unit of which was connected to the national grid in 2013.
- It is now operating under the one-year warranty maintenance period, which will last until the end of 2015.
7)Terrorism
- UN Convention on International Terrorism : This convention is sponsored by both India and Russia
- Both countries suffer from Terrorism : India from Kashmir and Russia from Chechnya
8)Space
- GLONASS : Global positioning system of Russia..We adopted it prior to IRNSS
ISSUES Between India and Russia
a)Russia – Pak Nexus
- Joint Military exercise
- Also they have exchanged first ever foreign office consideration
- Russia was against India’s concept of SAARC – 1 and promotion of Sub regionalism
- MoU on the usage of Gwadar Port by Russia
b)Increasing Russia – China Cooperation
- First ever military exercise in Ural Mountain
- Defence agreement signed
- China’s critical support to Russia on Syrian issue
- Growing joint energy exploration between both
