Biotic Interaction :
Definition :
- In ecology, a biological interaction is the effect that a pair of organisms living together in a community have on each other.
- The interaction among organisms within or between overlapping niches can be characterized into five types of relationships
- Competition
- Predation
- Commensalism
- Mutualism
- Parasitism
Competition
Definition :
- When two or more organisms in the same community seek the same resource (e.g., food, water, nesting space, ground space), which is in limiting supply to the individuals seeking it, they compete with one another.

Intraspecific competition:
- If the competition is among members of the same species, it is called intraspecific.
Interspecific competition :
- Competition among individuals of different species it is referred to as interspecific competition.
Within a species, either all members obtain part of a necessary resource such as food or space, or some individuals obtain enough for their needs while other members, cut off from the resource, die or are forced to inhabit a less suitable or marginal area. Young members of a population are most often adversely affected.
Example .
- For example, two male birds of the same species might compete for mates in the same area.
Predation :
- Predation occurs when an organism kills and consumes another organism.
- Herbivory is a form of predation in which the prey organism is a plant.
- There are four commonly recognized types of predation (1) carnivorous, (2) herbivorous, (3) parasitism, and (4) mutualism. Each type of predation can by categorized based on whether or not it results in the death of the prey.
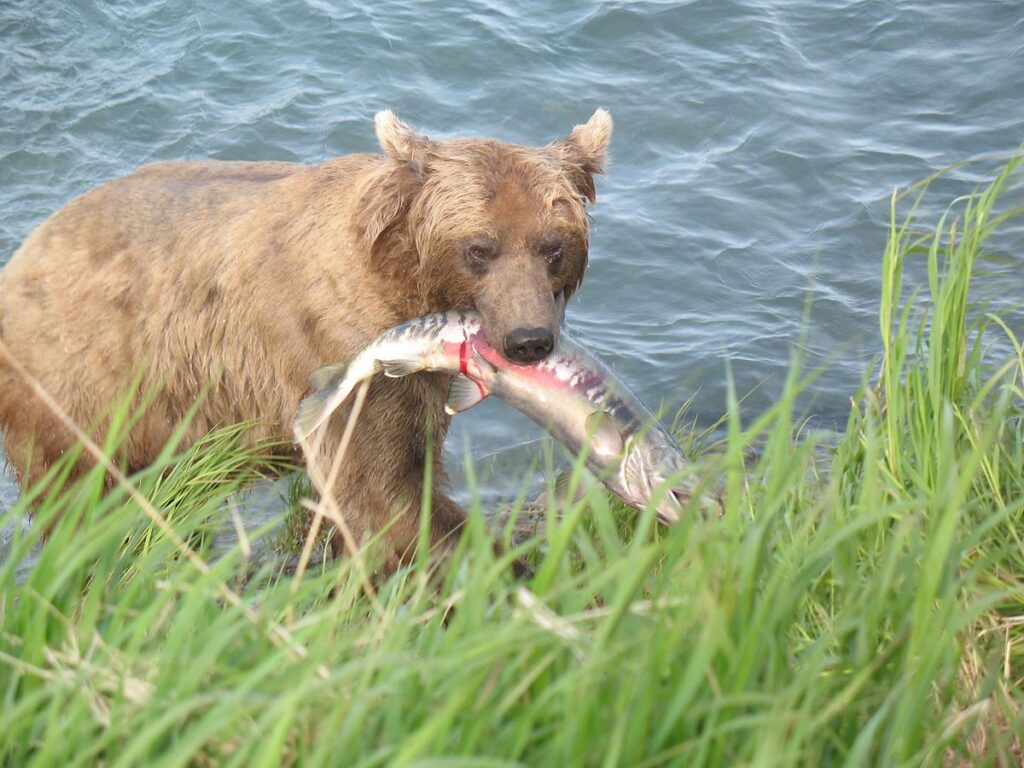

Examples :
Think of wolves hunting moose, owls hunting mice, or shrews hunting worms and insects.
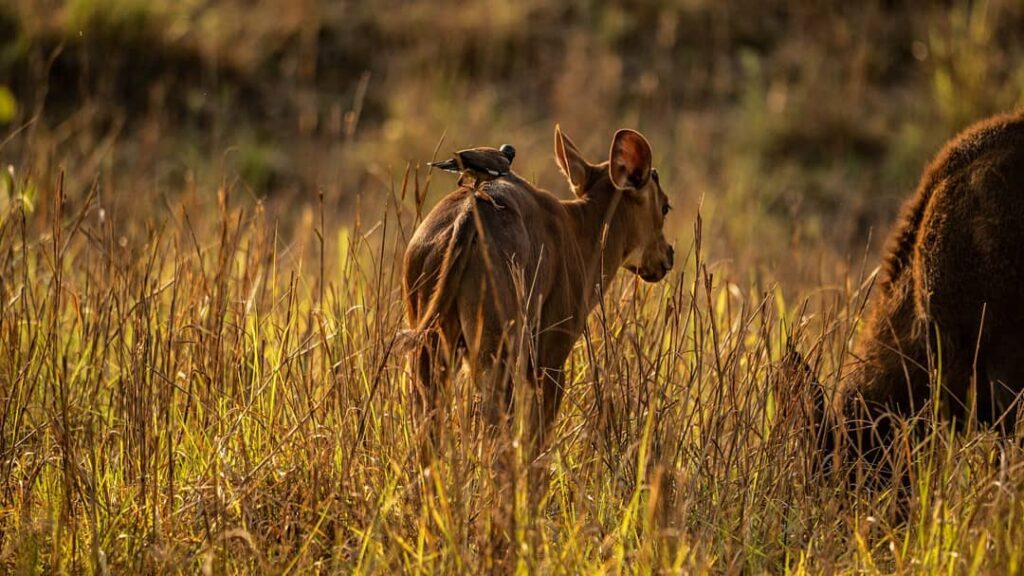
Commensalism
It is an association between two organisms in which one benefits and the other derives neither benefit nor harm.
Examples
- Remora fish have a disk on their heads that makes them able to attach to larger animals, such as sharks, mantas, and whales. When the larger animal feeds, the remora detaches itself to eat the extra food.
- Birds that live in the hollows of trees are commensal. Their presence generally does no harm to the tree, but the tree provides the bird with shelter and protection.

Mutualism :
- Mutualism, association between organisms of two different species in which each benefits.
- Mutualistic arrangements are most likely to develop between organisms with widely different living requirements.
Examples
The bee and the flower.
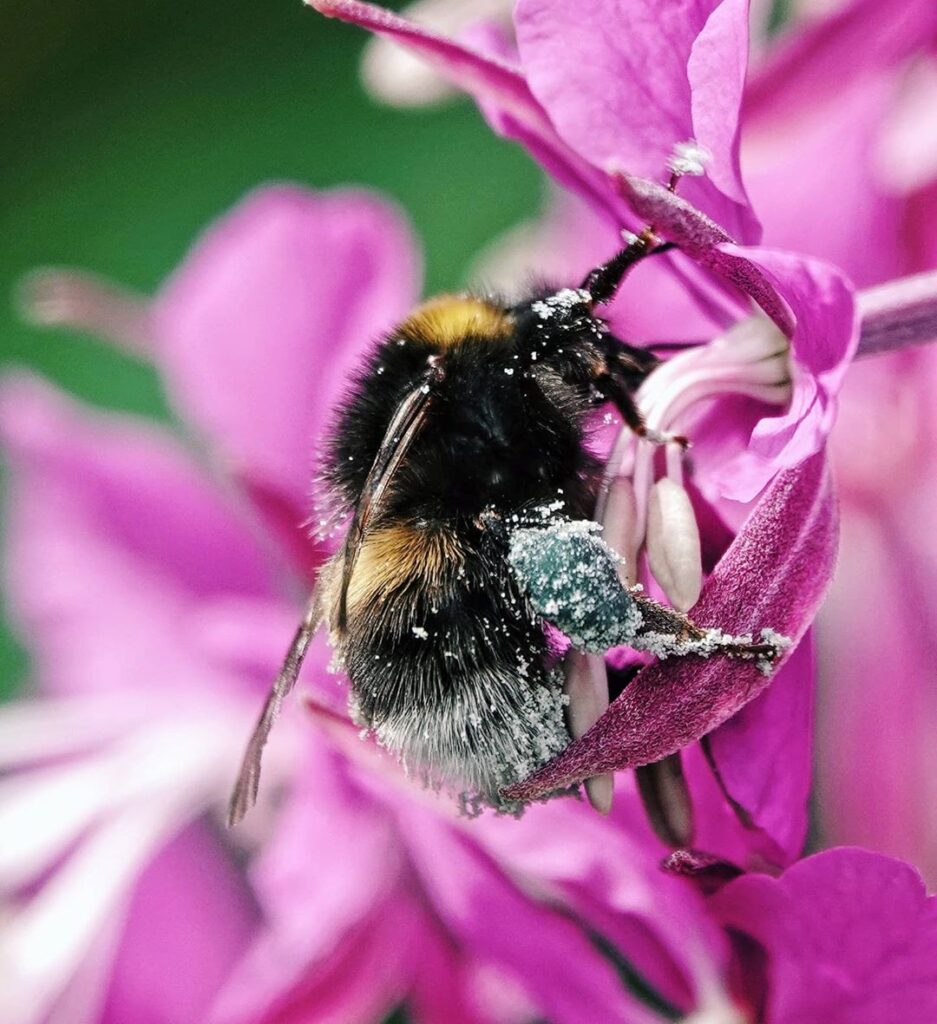

When they land in a flower, the bees get some pollen on their hairy bodies, and when they land in the next flower, some of the pollen from the first one rubs off, pollinating* the plant. This benefits the plants. In this mutualistic relationship, the bees get to eat, and the flowering plants get to reproduce.
Other examples
- The spider crab and the algae.
- The bacteria and the human.
Parasitism
- parasitism is a symbiotic relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or in another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life.
- Fleas or ticks that live on dogs and cats are parasites. They are living off of the blood of the host animal.