Narmada River
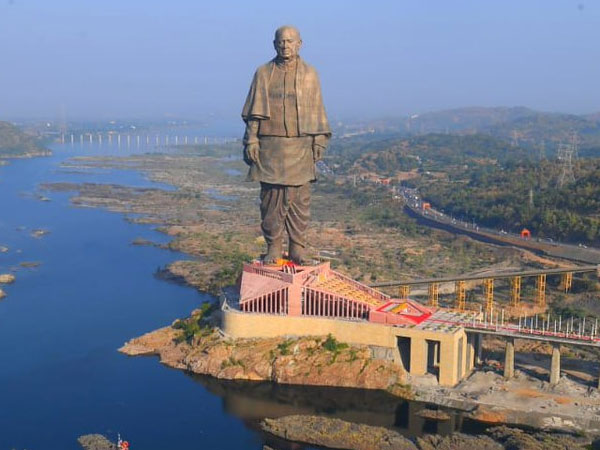

- Narmada is the largest west flowing river of the peninsular India.
- Narmada basin lies in the states of Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh.
- The total area of this river basin is 98,796 Sq.km.
It is bounded by
1.the Vindhyas on the north,
2.the Maikala range on the east,
3. the Satpuras on the south
4.the Arabian Sea on the west.

Fig : Satpura and Vindhya Range Source : Patrika
Source of the river
- It rises from Maikala range near Amarkantak in Anuppur district of Madhya Pradesh.
- Narmada drains into the Arabian Sea through the Gulf of Khambhat.
- The major part of basin is covered with agriculture accounting to 56.90%.
Tributaries
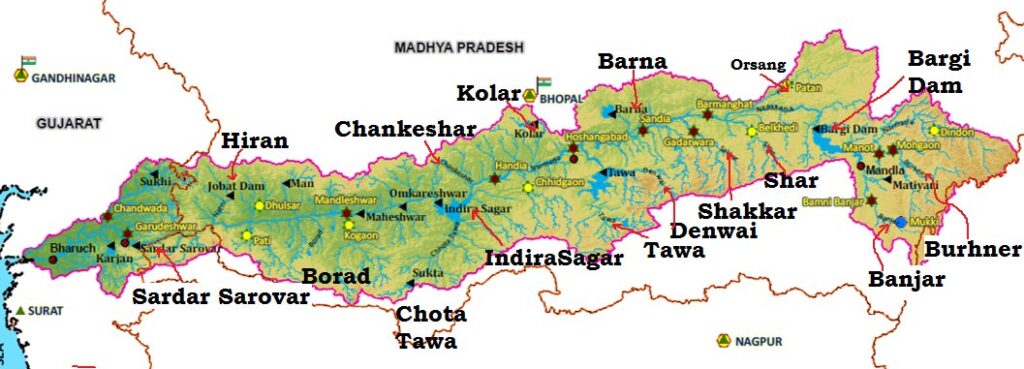
Fig : Narmada river Map Source : WRIS
Left Tributaries
- The Burhner
- The Banjar
- The Sher
- The Shakkar
- The Dudhi
- The Tawa
- The Ganjal
- The Kundi
- The Goi
- The Karjan
Right Tributaries
- The Hiran
- The Tendoni
- The Barna
- The Kolar
- The Man
- The Uri
- The Hatni
- The Orsang
The Narmada Water Disputes Tribunal has allocated the Narmada water(75% dependable utilisable flow of 34.54 cubic Km at Sardar Sarovar dam) amongst the States
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Rajasthan
- Gujarat
The major Hydro Power Project in the basin are Indira Sagar, Sardar Sarovar, Omkareshwar, Bargi & Maheshwar.
Dams in Narmada river
- Sardar Sarovar Dam- Gujarat
- Indira Sagar Dam – Madhya Pradesh
- Omkareshwar Dam – Madhya Pradesh
- Maheshwar Dam – Madhya Pradesh
- Bargi Dam – Madhya Pradesh
- Maan Dam – Madhya Pradesh
- Jobat Dam – Madhya Pradesh
- Tawa Dam – Madhya Pradesh

Fig : Sardar Sarovar Dam
